Google releases the most popular and trending word or celebrity each year. It counts the number of times a word has been searched for or how many times a word appeared in a string of searches. Google alone handles more than 40,000 search queries per second which, over a year, would be a data storage nightmare. But thanks to improved hardware and efficient cooling systems, data is intact in the vast data centres.
In the early days of the internet, two decades ago, identifying the most searched entity was not an easy job. Hashing was introduced by the researchers at AT&T, a statistical technique which transforms data into random value uniformly distributed over some interval. Two similar elements will be stored in the same bin. The distinction between the elements is estimated from the probability that a given bin remains empty. There have been many innovations to finding the frequencies of items in a stream of data.
With increasing internet usage, the data generated too has increased. Back in the day, data might have been an area of concern for a few entities. Now, data is being used for almost all purposes from recommending movies to predicting presidential candidate from sentiment analysis on Twitter.
The commonality in these applications is the continuous stream of data that is being exchanged back and forth. To analyse this data and to make sense of it in real time, is an arduous task.
To address this issue, the researchers at MIT’s CSAIL, developed a method which uses machine learning models to make guesses about the frequency of the data. This is the first of its kind streaming algorithms which employ machine learning.
The main objective behind the proposal of these new class of algorithms is to keep track of the frequencies of certain items in a stream of data. These items can be trending topics on Twitter or popular searches on Google.
The researchers call this method “LearnedSketch”, which is trained on 210 million data packets from a Tier 1 ISP and run on 3.8 million AOL queries.
The main focus here was on a class of hashing based algorithms like Count-Min and Count-Sketch. The team define what they call as a Heavy-hitter oracle within the subsets of the bins that store these frequently appearing items from packets of data streamed. This
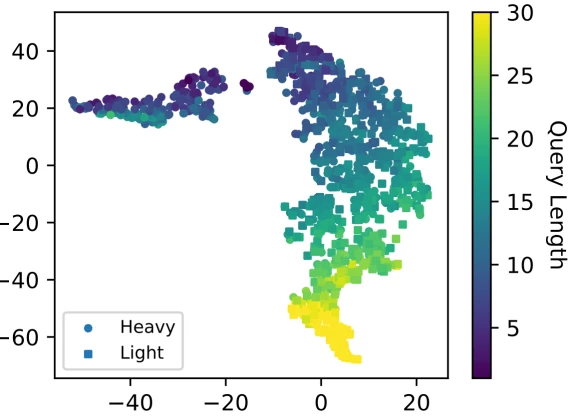
The above scatter plot is a visualisation of the embedding space learned by the model on Internet traffic data, where each point represents one network flow. For example, if there is a word say, “machine learning”, that appears frequently in the dataset. The model can be made to remember such popular words for predicting. But, there are always other factors that contribute to the popularity.
Model Construction For Search Query Estimation:
- A neural network is trained to predict the number of times a search phrase appears(AOL queries)
- To process this, a recurrent neural network(RNN) is trained with LSTM which takes these search phrases as inputs.
- The character IDs(lower or upper case, punctuation marks etc) are mapped to embedding vectors before being fed to RNN
- The final states encoded by the RNN are fed into a fully-connected layer to predict the frequency of a certain search phrase.
Key Takeaways
- Learning based algorithms reduced estimation errors by 18% to 71% when compared to non-learning based algorithms like Count Min.
- This model can identify items which go unnoticed with conventional methods.
- A full-length application would enable the users to follow spikes in web-traffic and exploit these results say, for improving e-commerce sites and other customer based recommendation platforms.
Read more about the experiment here