The ability to capture and successfully garner insights from their data have led many enterprises across the world to streamline their processes and boost their growth. Data analytics has become the norm across functions like Marketing, Retail, Operations and Finance. However, a domain as important and as ubiquitous as Human Resource has woken up to data analytics very recently. The adoption rate is still low with the required expertise missing in most organizations, yet there is ample buzz around this area.
So what exactly is HR Analytics?
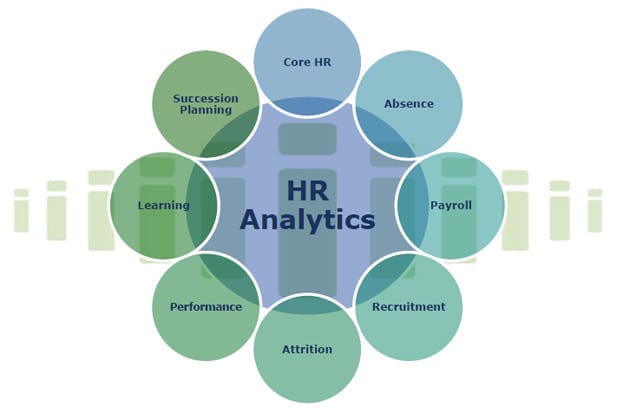
Human Resource analytics is the application of sophisticated data mining and business analytics techniques to human resources data. Simply put, it is figuring out the what, when, why, how and where of HR functions like recruitment, training, retention, performance measure and engagement.
HR Analytics, also known as Talent Analytics, People Analytics or Workforce Analytics, enables the HR Manager to go over and above her gut-feel and helps her to take decisions based on hard-core data.
Benefits of HR Analytics
More than often most of the data that is required for such an analysis is already there within the organization. Age, academic history, demographics, prior experience, trainings undertaken, performance ratings and many such data points are already available with the HR department. This internal data is combined with external data sources to get a complete picture. HR Analytics helps in putting all this data together, marry it with relevant external data and help HR Managers ask relevant questions so as to take better decisions.
Some questions which HR Analytics helps find answers to:
- Figure out the reason behind a high turnover in a certain team
- Why is the top talent quitting at a higher rate than others?
- How to improve productivity of a team?
- Skill-gaps in the organization and how to fill those
- The effectiveness of the employee orientation (or similar) program
- Predict the right people to hire for a specific role
- Predict and manage attrition rate
- What drives employees across gender, age, country, etc.?
- Does the performance rating system actually reflect employee performance?
- How to attract a more diverse workforce?
HR Analytics has benefits across reactive, proactive, strategic and predictive decision-making.
Key Players in the HR Analytics space
A research conducted by Bersin by Deloitte in 2014, show that the HR Analytics software “market grew by 17% last year and is now over $5 billion in size.” Huge vendors such as Oracle, IBM, SAP and Workday compete with more specialized players such as PeopleFluent, Talent Analytics , Saba, Visier and Cornerstone to deliver HR analytics software as a service.
- SAP offers SuccessFactors Workforce Analytics and SuccessFactors Workforce Planning. They help in predicting retention and provides extensive modelling capabilities for workforce planning.
- Powered by Watson Analytics, IBM Kenexa Talent Analytics enables HR professionals to simply type in what they want to see from their talent data and the results are displayed as an easy to interpret visualization.
- Saba’s cloud-based Intelligent Talent Management solution uses machine learning to improve the way HR professional hire, develop, engage and inspire people. The solution also comes with predictive capabilities to cut through the noise and prioritize the most important and relevant information.
- HiQLabs uses public data, internal company data, or a combination of both for its predictive models.
- Workday’s on-demand HCM solution unifies HR and Talent Management into a single system-of-record to help reduce costs, gain operational visibility and prepare organizations’s for future shifts.
HR Analytics in Action
Many organizations who have deployed HR Analytics have successfully reaped the benefits from the same too.
Black Hill Corporation uses HR Analytics to Prevent a Massive Turnover Catastrophe
In an HBR article, Mick Collins highlights how Black Hill Corp. used HR Analytics to their advantage.
Black Hills Corp. is a 130-year-old energy conglomerate, which doubled its workforce to about 2,000 employees after an acquisition. Like many energy companies, a combination of challenges — an aging workforce, the need for specialized skills, and a lengthy timeline for getting employees to full competence — created a significant talent risk. In fact, forecasts showed that, within five years, the firm could lose 8,063 years of experience from its workforce.
To prevent a massive turnover catastrophe, the company used workforce analytics to calculate how many employees would retire per year, the types of workers needed to replace them, and where those new hires were most likely to come from. The result was a workforce planning summit that categorized and prioritized 89 action plans designed to address the potential talent shortage.
Ameriprise Financial’s Integrated Approach to Talent Investments
Collins quotes another case study on Ameriprise Financial from Transformative HR. Ameriprise Financial is a diversified financial services company spun off from American Express in 2005.
When the newly formed firm began delivering a set of HR activities such as on boarding, training and performance reviews, employee feedback rated the quality of these services as “poor.” Furthermore, Ameriprise Financial had no framework for allocating HR time to talent issues with highest impact.
To improve their HR functions, Ameriprise began to integrate workforce and financial data to align talent investments with business results, and more proactively develop data-driven insights used to predict turnover, reduce new hire failure rates, and manage persistent poor performers. Employee feedback was overwhelmingly positive, with HR transforming from “order taker” to “key business contributor.”
Google’s use of People Analytics for Effective Decision Making
In an article published in TLNT, Dr John Sullivan, an internationally known HR thought-leader, lists some of Google’s past and current data-driven people management practices.
The people analytics team at Google reports directly to the VP and it has a representative in each major HR function. It produces many products, including employee surveys that are not anonymous, and dashboards. It also attempts to identify insightful correlations and to provide recommended actions. The goal is to substitute data and metrics for the use of opinions.
Some of Google’s initiatives in people analytics include:
Project Oxygen: Helped them identify the eight characteristics of great leaders. The data proved that rather than superior technical knowledge, periodic one-on-one coaching which included expressing interest in the employee and frequent personalized feedback ranked as the No. 1 key to being a successful leader.
PiLab: A unique subgroup that conducts applied experiments within Google to determine the most effective approaches for managing people and maintaining a productive environment (including the type of reward that makes employees the happiest).
A retention algorithm: Google developed a mathematical algorithm to proactively and successfully predict which employees are most likely to become a retention problem.
Predictive modelling: Google develops predictive models and uses “what if” analysis to continually improve their forecasts of upcoming people management problems and opportunities. It also uses analytics to produce more effective workforce planning, which is essential in a rapidly growing and changing firm.
An effective hiring algorithm: It developed an algorithm for predicting which candidates had the highest probability of succeeding after they are hired.
To sum up, with data-backed decisions becoming key to survival, more and more HR management software will have in-built analytics to help managers seek answers to their questions. However, HR Teams will also have to upgrade their number crunching skills so as to ask the right questions from their data.